What You Need to Know About Anti-Fog Safety Glasses
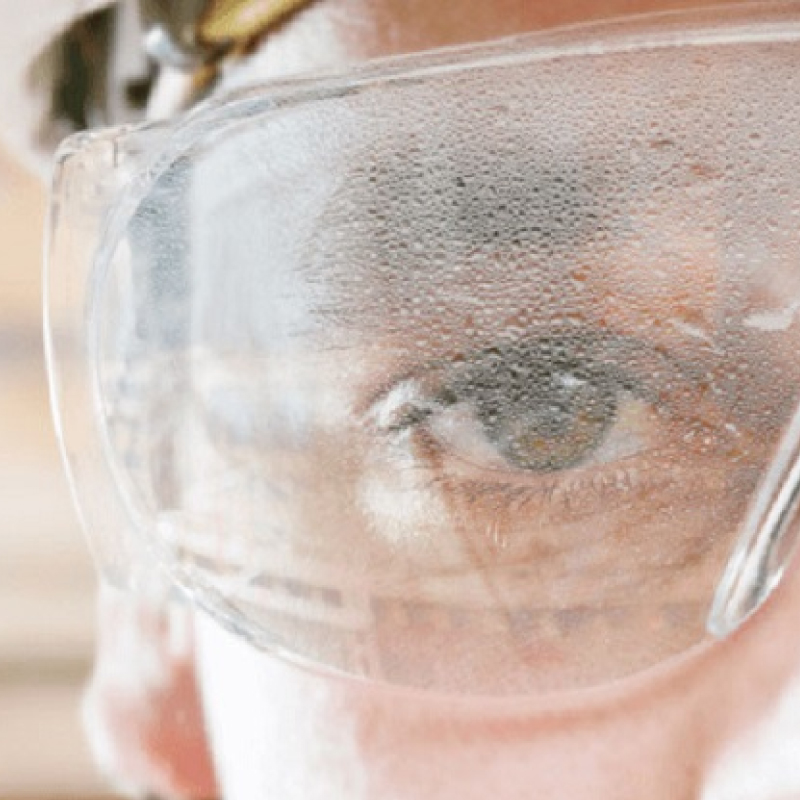
Foggy lenses are something most glasses wearers have dealt with in the last year during the COVID-19 pandemic. Those who have always needed PPE for their jobs have been dealing with this issue for even longer. Fogging eyewear is a huge inconvenience and safety risk to those workers. In fact, fogging lenses are the number one reason workers remove or do not wear safety eyewear.

What You Need to Know About Anti-Fog Safety Glasses en
20/12/2022
Foggy lenses are something most glasses wearers have dealt with in the last year during the COVID-19 pandemic. Those who have always needed PPE for their jobs have been dealing with this issue for even longer. Fogging eyewear is a huge inconvenience and safety risk to those workers. In fact, fogging lenses are the number one reason workers remove or do not wear safety eyewear. Luckily, there is a solution in the form of anti-fog safety glasses. Before we dive into the science of anti-fog, it is important to understand the cause of fog itself.
What Causes Fogging?
Fogging lenses can be caused by several factors. It is first crucial to understand what the fog actually is. Regardless of its cause, fog is the result of water vapor that has condensed into fine droplets and collected on the lens. This is typically because the lens is cooler than the air around it. Why would this be? There are several potential reasons:
*Humidity. An abundance of warm, moist air is one of the most common causes of eyewear fog. Whether working outdoors or in purposefully humid environments, warm air will collide with the cooler eyewear and cause it to fog.
*Temperature change. Drastic changes in temperature are another common cause of fogging lenses. Going from a cold location such as a refrigerated unit or even just an air-conditioned indoor location to a warmer one will cause air to condense.
*Body heat. People working in warm environments or those exerting a large amount of physical force might also have to deal with fogging lenses due to their body increasing the temperature of the air around them. Sweat may also drop on eyewear and be treated similarly to fog.
*Face coverings. Some face coverings—especially when improperly worn—cause warm breath to go up into the orbital cavity. This has become increasingly more common as people wear masks to protect themselves from COVID-19. While not a direct cause, washing anti-fog safety glasses can also increase fog risk, as water and soap can rub off some anti-fog coatings. For that reason, it is always important to follow manufacturers’ instructions for proper care of anti-fog safety glasses. Every manufacturer will have different rules on how to clean their lenses based on the type of anti-fog used as well as the material the eyewear is made of. Following these guidelines is the best way to maintain the integrity and longevity of your anti-fog eyewear.
History of Anti-fog Technology
Like so many scientific innovations, anti-fog safety glasses have NASA to thank for their invention. In the 1960s, NASA was worried that astronauts would be put at risk due to fogging visors when exploring space. During a spacewalk, Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan tested their newly invented anti-fog technology and found that his helmet visor fogged in reaction to the atmosphere, except for where an anti-fog solution had been applied. From there, anti-fog technology developed and became available in many forms such as sprays, gels, wipes and coatings applied during the manufacturing process. The latter solution is considered one of the most effective and long term for today’s workers. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, more workers than ever are wearing face coverings, even when not necessary for the completion of their job. This has caused a huge increase in demand for anti-fog safety glasses and solutions. PPE manufacturers are working to increase the availability of anti-fog eyewear.
The Science of Anti-Fog Safety Glasses
The latest anti-fog technology manipulates moisture on the surface of the lens through lens-coating agents. There are several types of products that can be used for this, such as surfactants, detergents, polymers, hydrogels, colloids and nanoparticles. Currently, there are two major categories of these coatings: hydrophobic and hydrophilic. While both are effective at managing fog, they have different functions.
Hydrophobic means “water fearing.” This type of coating repels water causing it to run off the lens. It is best for high moisture environments and those where workers are regularly transitioning between environments with varying temperatures.
Hydrophilic means “water loving.” With this type, water is absorbed by the coating. Eyewear featuring this anti-fog is best for moderate moisture environments. Both coating types can adequately serve various anti-fog needs.
Coatings are added to anti-fog safety glasses in a variety of ways, most commonly through dip and flow processes. The decades-old dip process enables agents to adhere to both sides of the lens as they are dipped in the coating. On the other hand, the flow process coats one side at a time, which allows for different agents to be cured on each side if desired. Other methods for lens-coating include spray and spin processes, which are rarely used for anti-fog safety glasses.
Anti-Fog Safety Standards
Until 2020, there was no U.S. safety standard for anti-fog safety glasses. This meant that any manufacturer could claim to have a high-quality anti-fog product with no way to measure its effectiveness and longevity. While Europe does have a safety standard for anti-fog safety glasses (EN166) this standard only states that glasses must specify which coatings are applied and contains test protocols. Longevity is not addressed by that standard. Last year, the International Safety Equipment Association (ISEA) created a US standard (ANSI Z87.1-2020) for anti-fog safety glasses. The standard mandates that eyewear can only be classified and marked as anti-fog if lenses remain fog-free for at least eight seconds. Having an ANSI standard means that U.S. workers and safety coordinators can purchase anti-fog safety glasses knowing that they are getting a quality, tested product. Approved eyewear will be designated by an “X” on the lens.
The Cost of Fogging Lenses
Any risk management officer or company safety coordinator can spell out the potential problems that occur due to fogging lenses. As mentioned, it is the top reason for safety eyewear to be removed or not worn at all. In many of these work environments, safety glasses aren’t just smart to wear, but mandated by OSHA or other regulatory bodies. Not wearing safety equipment can put the company at risk financially and the worker at risk both physically and financially. Let’s start with the worker. The biggest risk is, of course, injury. Safety eyewear manufacturers frequently receive messages from customers with stories about how eyewear saved their eyes. Safety eyewear protects workers’ eyes from chemicals, debris, heat and other elements that can impair or totally take away their vision. When accidents happen due to a lack of safety eyewear, workers must deal not only with the injury, but also costs (medical, legal, etc.) associated with the injury and potential lost income in the future. Some of these costs are passed to the company both directly and indirectly. The US Bureau of Labor estimates that eye injuries cost employers $467 million per year in direct costs. The amount of indirect costs (legal fees, recruiting and training new workers, etc.) is close to $934 million annually, according to NIOSH. NIOSH also estimates that there are an average of 2,000 job-related eye injuries every day. Even when injury doesn’t occur, fogging eyewear can still cost companies. Workers removing their eyewear can lead to big fines for businesses that are found non-compliant with safety standards. Because eyewear is readily visible, it is an easy violation for inspectors to cite. When workers do wear safety glasses, time and productivity can be lost when they have to take time away from their jobs—sometimes even to go to a safer environment—in order to wipe the fog off their lenses.
Who Needs Anti-Fog Safety Glasses?
There are many industries where workers benefit from anti-fog safety glasses. At present there is a growing demand in the healthcare industry as medical workers wear full PPE to treat patients and protect themselves from COVID-19. Outside of the healthcare sector, there are several industries who need anti-fog eyewear in COVID and non-COVID times. Construction is one big industry that needs anti-fog safety glasses. Body heat and humid temperatures in the summer months mean that eyewear has a big potential for fogging. Injury risk is heightened by the use of powerful tools. Food service and processing plants are another industry that rely on anti-fog eyewear. These plants often have zones of varying temperature and some humid environments. Energy sector workers also benefit greatly from anti-fog safety glasses. Those in the oil and gas industry certainly need anti-fog eyewear—especially those who work in mines with limited airflow and intense conditions. Anti-fog technology continues to see innovations in order to better serve the workforce. With a growing need for such technology and serious risks at play, anti-fog safety glasses are more important than ever. PPE manufactures like Pyramex are working to expand their anti-fog options and create a diverse selection of eyewear to fit workers in any and every environment.
Source: OH&S